Treatment of burns
Narrowly defined burns generally refer to the damage of various heats to the body tissues, including flame burns, hot metals, and hydrothermal burns. Some non-thermal factors such as electricity, chemicals, radiation, etc. can also cause the body tissue to suffer from similar burns, called generalized burns.
Burns are common injuries in daily life, but wounds of burns are highly susceptible to infection, complicated treatment, long healing time, scarring of scar contracture and dysfunction after healing, and extensive burns can cause changes in systemic conditions and visceral damage. There is shock, sepsis, etc., and the mortality rate is high.
Therefore, it is necessary for the doctors at the basic level to learn the judgment of burn injuries, the changes in the body tissues after burns and the treatment methods, and the timely treatment that can be handled. If they cannot be processed, they should be transferred to the specialist hospital for treatment as soon as possible. Remember that time is life.
Don't panic when you have a burn, don't be careless. Firstly, the injury judgment and indexing of the burn are carried out, and the area and depth of the burn are judged whether there is an inhalation injury or a combined injury, the age of the patient and the health before the injury, and whether the wound has to be contaminated after the injury.
I. burn
Only the superficial epidermis is damaged, the basal cells are not damaged, and the skin is red, and no special treatment is needed. However, it is necessary to judge the wound condition and protect the wound surface. About 3 days after the injury, redness, swelling, and pain disappeared, and desquamation was healed. If the patient has a burning sensation, apply a thin layer of oil or a traditional Chinese medicine ointment.
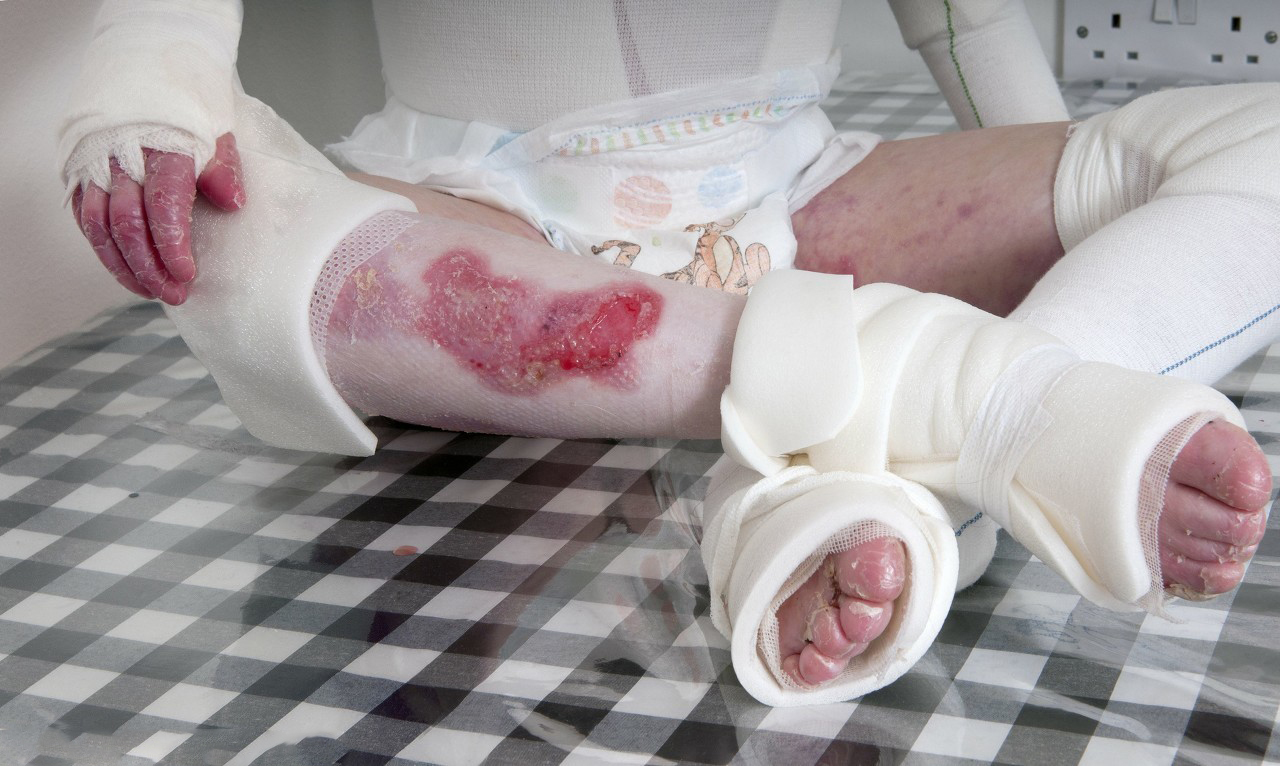
Shallow II. Burn (vesicular burn)
Injury to the epidermis and dermal papilla, plasma-like liquid accumulates between the epidermis and the dermis, forming blisters, the base of the wound is light red, with red spots between them, hyperalgesia is severe pain, and edema is obvious. Small area of shallow II.
Burns, if the blister skin is intact, should be preserved and should not be easily removed. The blister skin can protect the wound, relieve pain and promote wound healing. Simply use a disposable syringe to aseptically remove the effusion from the blister immediately, then sterilize and wrap.
If the blister skin has been torn off, it can be wrapped with a sterile oily dressing. As for dressing change, frequent dressing changes are not recommended to reduce the damage of the newborn epithelium unless the dressing is wet or smelly or signs of infection are found. If the wound has been infected, the necrotic tissue and secretions should be removed in time to keep the wound clean.
Shallow II. Burns usually heal within 2 weeks after injury and there is hyperpigmentation after healing.
Deep II. burn
Due to skin damage deep into the dermis layer, the base surface is pale and the texture is tough. After the wound surface is gradually dried, a tiny vascular network plunger can be seen, which is dull and painless. It usually heals in 3-4 weeks. After healing, the epidermis is weak and thin, easy to break, easy to form small pustules, and can leave hypertrophic scars.
III. burn
It is the damage of the whole layer of skin, deep subcutaneous fat, muscle and bone damage. The wound is pale or esoteric, and the subcutaneous branches embolize the blood vessels, and the skin is inelastic and has no feeling. The healing time of III degree burns is often several months, and large wounds can only heal if they are surgically skinned.
Deep burn
Due to the large number of necrotic tissues, it is difficult to avoid tissue liquefaction and bacterial colonization. Therefore, topical antibacterial drugs (such as 1% sulfadiazine silver cream) should be properly selected, but topical antibacterial drugs can only inhibit bacterial growth to a certain extent. Areas of deep burn often have complications such as pulmonary complications, cardiac insufficiency, renal insufficiency, stress ulcers, cerebral edema, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to go to the burn specialist hospital for professional treatment. Remember, time is life!



